Magnetically Driven Photosensitive Nanorobots with Dual-Modal Imaging for Enhanced Photothermal-Photodynamic Cancer Therapy
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.64504/big.d.v2i4.298Abstract
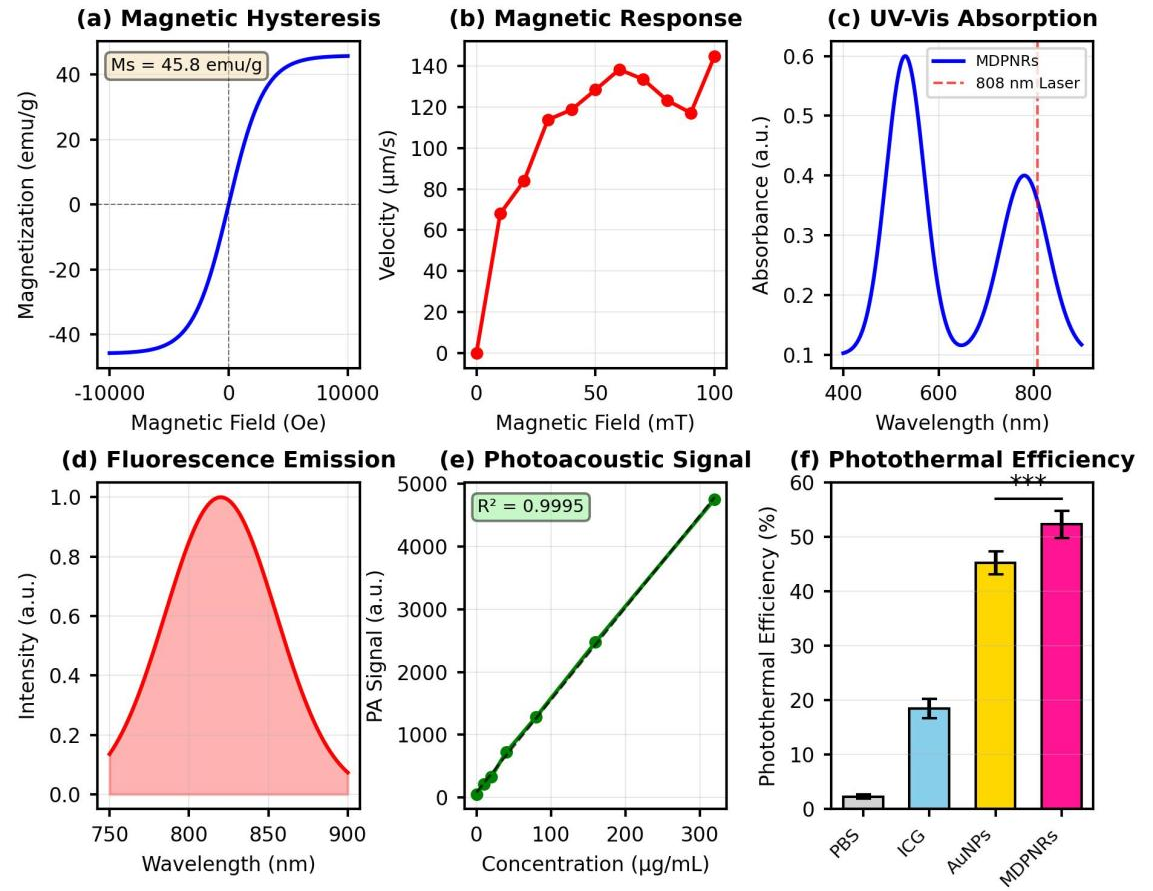
Conventional phototherapy for cancer faces significant challenges, including limited tissue penetration depth, poor tumor-targeting specificity, and suboptimal therapeutic efficacy, which hinder its clinical application. The development of intelligent nanorobotic systems that can be precisely controlled and monitored offers a promising avenue to overcome these limitations. In this study, we designed and fabricated a novel magnetically driven photosensitive nanorobot (MDPNR) for enhanced cancer therapy. The MDPNRs were constructed by integrating superparamagnetic iron oxide (Fe3O4) nanoparticles, plasmonic gold nanoparticles (AuNPs), and the photosensitizer Indocyanine Green (ICG) within a mesoporous silica nanoparticle (MSN) framework. This multifunctional design enables active tumor targeting under the guidance of an external magnetic field, combined with dual-modal imaging capabilities (fluorescence and photoacoustic imaging) for real-time therapeutic monitoring. Upon accumulation at the tumor site, the MDPNRs were activated by a single 808 nm near-infrared (NIR) laser, triggering simultaneous photothermal therapy (PTT) and photodynamic therapy (PDT). The synergistic action of localized hyperthermia and reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation was investigated for its enhanced tumor-killing effect. The synthesized MDPNRs showed a saturation magnetization of 45.8 emu/g (enabling magnetic response velocity up to 125.5 ), a high photothermal conversion efficiency of 52.3%, and 15-fold higher ROS generation efficiency compared to free ICG under 808 nm NIR irradiation (1.5 W/cm2). In a 4T1 breast cancer mouse model, the MDPNRs demonstrated remarkable tumor accumulation (>85% enrichment at the tumor site) under magnetic guidance. The dual-modal imaging provided clear visualization of the nanorobots’ biodistribution and therapeutic response. The combined PTT-PDT treatment resulted in significant tumor growth inhibition (>90%) and prolonged survival with negligible systemic toxicity. This work presents a sophisticated and precisely controllable nanorobotic platform that integrates active targeting, dual-modal imaging, and synergistic phototherapy. The MDPNRs offer a powerful strategy to enhance the precision and efficacy of cancer treatment, providing a solid foundation for future clinical translation.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Versions
- 2026-01-23 (2)
- 2025-12-09 (1)
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2025 BIG.D

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.